As a homeowner, you might at some point need to consider concrete scanning for your property. This may be due to an upcoming home repair project or the installation of underground services like pipes and conduits. Whatever the reason, understanding the different methods used for scanning concrete can help you ensure that any work is carried out efficiently and safely. In this blog post, we’ll take a look at the differences between traditional ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and concrete scanning such as x-ray. We will also discuss how each method works. Read on to learn more!
The Different Types of Concrete Scanning Methods
Concrete X-Ray
Concrete x-ray is a non-destructive testing method used to detect objects and flaws hidden inside the concrete. It can be used to find existing or potential problems, such as cracks, voids, air pockets, delaminations, honeycombing, and corrosion of reinforcing steel. This type of x-ray penetrates the concrete’s surface while emitting low doses of radiation which is then captured by a detector. The resulting images show the different densities of the material so that any weak points are clearly visible.
Concrete x-ray can also be used for dimensional analysis, to analyse rebar configuration and size as well as check for the presence or absence of post-tensioning cables and anchor bolts. By using this method it is possible to determine the condition of the structure before repairs take place. Concrete x-ray has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its accuracy in detecting imperfections that would otherwise remain hidden. This technology can also save time since it reduces labour costs associated with core sampling or chipping away concrete to reveal internal flaws. Additionally, it reduces safety risks associated with traditional methods since no personnel need to enter hazardous areas where radiation levels may be high.
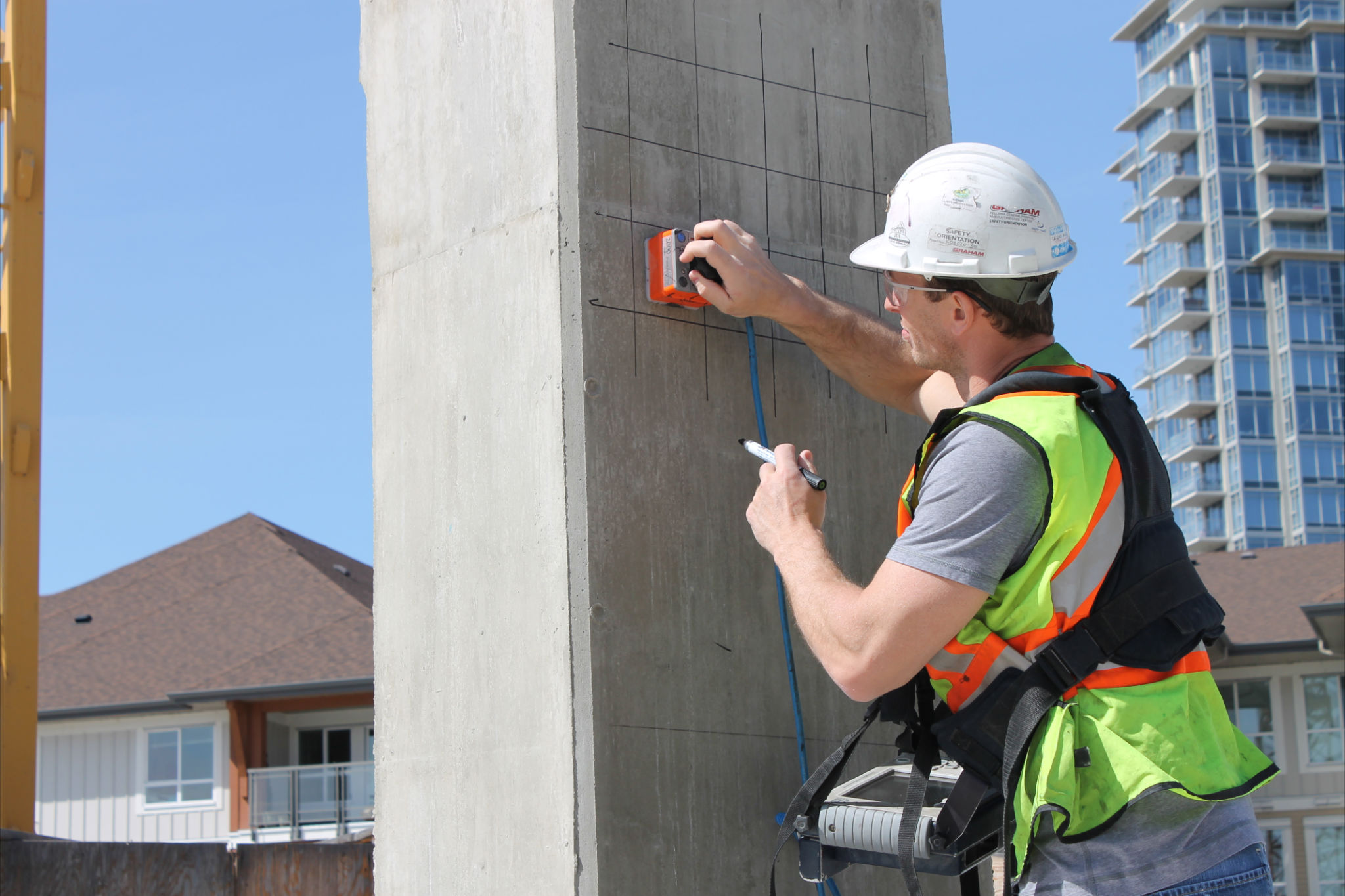
Concrete Scanning Ground Penetrating Radars (GPR)
Concrete scanning ground penetrating radars (GPR) is an invaluable tool for engineering and construction projects. This advanced technology allows professionals to look below the surface of a concrete slab or structure to identify any potential problems before they become expensive repairs or safety hazards. The radar works by emitting electromagnetic waves into the material, which bounce back with information about what lies within it. When used for concrete scanning, GPR can detect rebar and post-tension cables embedded in the concrete, as well as voids, delaminations, deterioration, and other issues hidden beneath the surface. It is especially useful for identifying imperfections that would not be detectable by other methods such as visual inspection or traditional X-ray techniques. Additionally, GPR can be used to inspect pavement structures like bridges and parking garages with non-destructive testing. The data collected helps engineers make informed decisions on structural repairs and assess liabilities before the risk factors become major issues. In short, GPR is a reliable technology offering contractors an efficient way to detect potential problems that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Which Is Better? GPR Or X-Ray?
Both GPR and x-ray technologies can be used for non-destructive testing, and it is not always easy to determine which of the two is the best option. GPR stands for ground penetrating radar, and it uses high-frequency radio waves that are sent into the ground, and then reflected back up to a surface receiver. This technology is capable of detecting objects or features in the subsurface of concrete, asphalt, or soil that cannot be seen by the naked eye. It can also provide information about the thickness and condition of buried concrete slabs and pipes. X-ray technology uses electromagnetic radiation to penetrate materials such as concrete, soil, and metal, allowing for an internal inspection of these materials. While x-ray technology may provide very detailed imaging results, it is limited in that it cannot penetrate thick materials or assess conditions below the surface without direct access to that area.
The choice between GPR and x-ray often comes down to what kind of imaging result is needed. If a more detailed image with more fine detail is desired, then x-rays are typically preferred over GPR due to their higher resolution capabilities. Conversely, if subsurface conditions need to be tested without further inspection is necessary, then GPR would likely be the better choice because it has a greater depth penetration than x-rays and can detect structures that are deeper underground. Additionally, if budget constraints are an issue, then GPR may also be more cost-effective than x-ray as it tends to be less expensive than its counterpart. Ultimately, when deciding which technology is best, there are many factors to consider before making a decision – from how much detail is needed from the imaging results to how much money can be spent – but with careful consideration either technology could get the job done well.
Do I Really Need To Have My Concrete Scanned?
If you are planning to perform any kind of construction, renovation, or demolition work on a concrete structure, it is always recommended that you have concrete scanning done first to determine the condition and composition of the concrete. Additionally, it can help to identify any potential obstructions that may be present beneath the surface. This will help ensure that your project can be carried out safely and successfully, preventing costly delays and ensuring that all relevant safety standards are met.
Conclusion
As illustrated, there are various methods for scanning concrete structures and it is important to choose the right one. For instance, X-Ray technology can detect major flaws in thick structures, while ground-penetrating radar is more suitable for detecting soft areas. GPR yields highly accurate results with a limited risk of radiation and should be used whenever possible if other scanning technologies don’t produce the desired results. Thermal imaging is also a reliable method, enabling the detection of temperature differences as an indicator of potential flaws and anomalies. Ultrasonic pulse velocity tests are especially effective in detecting concrete density and composition, thus making them ideal for structural assessment. Finally, acoustic emission can identify even slight damage in a structure by analysing vibrations caused by impacts or strains. Overall, concrete scanning is essential in helping ensure safe and lasting building projects, making selecting the right method critically important. For more information on concrete scanning, reach out to the experts at South East Scanning!